NEWS
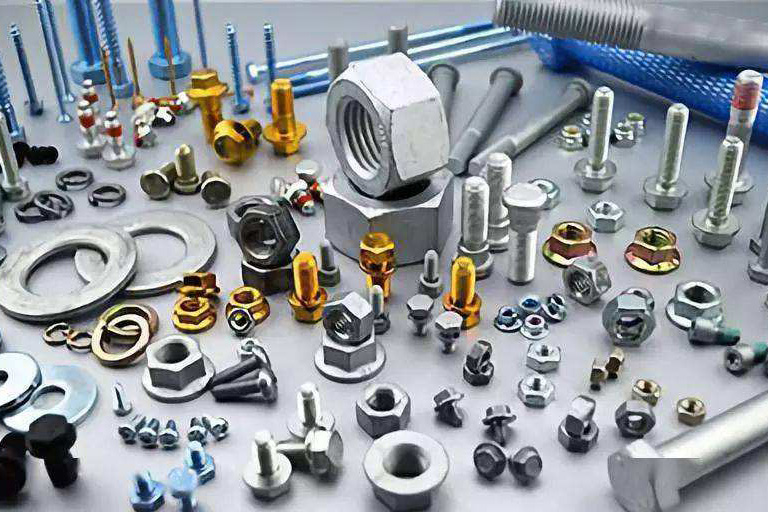
What is the difference between screws, bolts and nuts?
Time:2022-01-10(1) Bolts:
A type of fastener consisting of a head and a screw (a cylinder with an external thread), which needs to be matched with a nut to fasten and connect two parts with through holes. This type of connection is called bolt connection. If the nut is unscrewed from the bolt, the two parts can be separated, so the bolt connection is a detachable connection.
(2) Screws:
A class of fasteners consisting of a head and a screw can be divided into three categories according to their purpose - machine screws, set screws and special purpose screws. Machine screws are mainly used for a fast connection between a part with an internal threaded hole and a part with a through hole, without the need for nut matching (this connection form is called screw connection, which is also a detachable connection; also It can be matched with a nut to fasten the connection between two parts with through holes. The set screw is mainly used to fix the relative position between the two parts. The special purpose screw has a lifting ring screw for hoisting parts.
The material is 316 corrosion-resistant stainless steel, followed by 304. This is followed by carbon steel, which is also the most versatile material.
What are the standards and uses of hex nuts? As a standard part, nuts and blind rivets have their own standards. The editor summarizes the standards of hexagon nuts for distinction and connection and their uses.
For hex nuts, commonly used standards are:
GB41 Type I Hex Nut - Grade C
GB6170 Ⅰ type hexagon nut - A, B grade
GB6171 Type I Hex Nut - Fine Thread - Grade A, B
GB6172 Hexagon Thin Nuts - Grades A and B - Chamfering
GB6173 Hexagon Thin Nuts - Fine Thread - Grade A, B
GB6174 Hexagon Thin Nuts - Grade B - No Chamfer
GB6175 Ⅱ type hexagon nut - A, B grade
GB6176 Type II Hex Nut - Fine Thread - Grade A, B
GB6177 Hexagon Flange Nuts—Class A
GB55 Hexagon Thick Nut
GB56 Hexagonal Extra Thick Nut
GB1229 Big Hex Nut (High Strength for Steel Structure)
1. Ordinary outer hexagon nut:
It has a wide range of applications, and is characterized by a relatively large tightening force. The disadvantage is that there must be enough operating space during installation. During installation, an adjustable wrench, an open-end wrench or an eyeglass wrench can be used. All of the above wrenches require a large operating space.
2. Cylindrical head hexagon nut:
It is the most widely used of all screws, because its tightening force is relatively large, and it can be operated with an Allen wrench. It is very convenient to install and is used in almost all kinds of structures. The appearance is more beautiful and neat, but the disadvantage is that the tightening force is slightly lower than The outer hexagon, and the inner hexagon can be easily damaged due to repeated use and cannot be disassembled.
3. Pan head hexagon nut:
It is rarely used in machinery, and its mechanical properties are the same as above.
4. Headless hexagon socket nuts:
It must be used on certain structures, such as the top wire structure that requires a large jacking force, or where the cylindrical head needs to be hidden.
5. Countersunk head hexagon nut:
Mostly used in power machinery, the main function is the same as the inner hexagon.
6. Nylon lock nut:
A nylon apron is embedded in the hexagonal surface to prevent the thread from loosening, and it is used on strong power machinery.
7. Flange nuts: mainly play the role of increasing the contact surface with the workpiece, mostly used in pipes, fasteners and some stamping and casting parts.